In Collaborator Why the First Upload Is Not Displayed in Ui
Collaborating
Overview
Teaching: 25 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How can I utilise version control to collaborate with other people?
Objectives
Clone a remote repository.
Collaborate by pushing to a common repository.
Describe the basic collaborative workflow.
For the next stride, get into pairs. One person volition be the "Owner" and the other will be the "Collaborator". The goal is that the Collaborator add changes into the Possessor's repository. We will switch roles at the finish, and then both persons will play Possessor and Collaborator.
Practicing Past Yourself
If you're working through this lesson on your ain, you can carry on by opening a second terminal window. This window volition represent your partner, working on another computer. You won't need to give anyone access on GitHub, because both 'partners' are you lot.
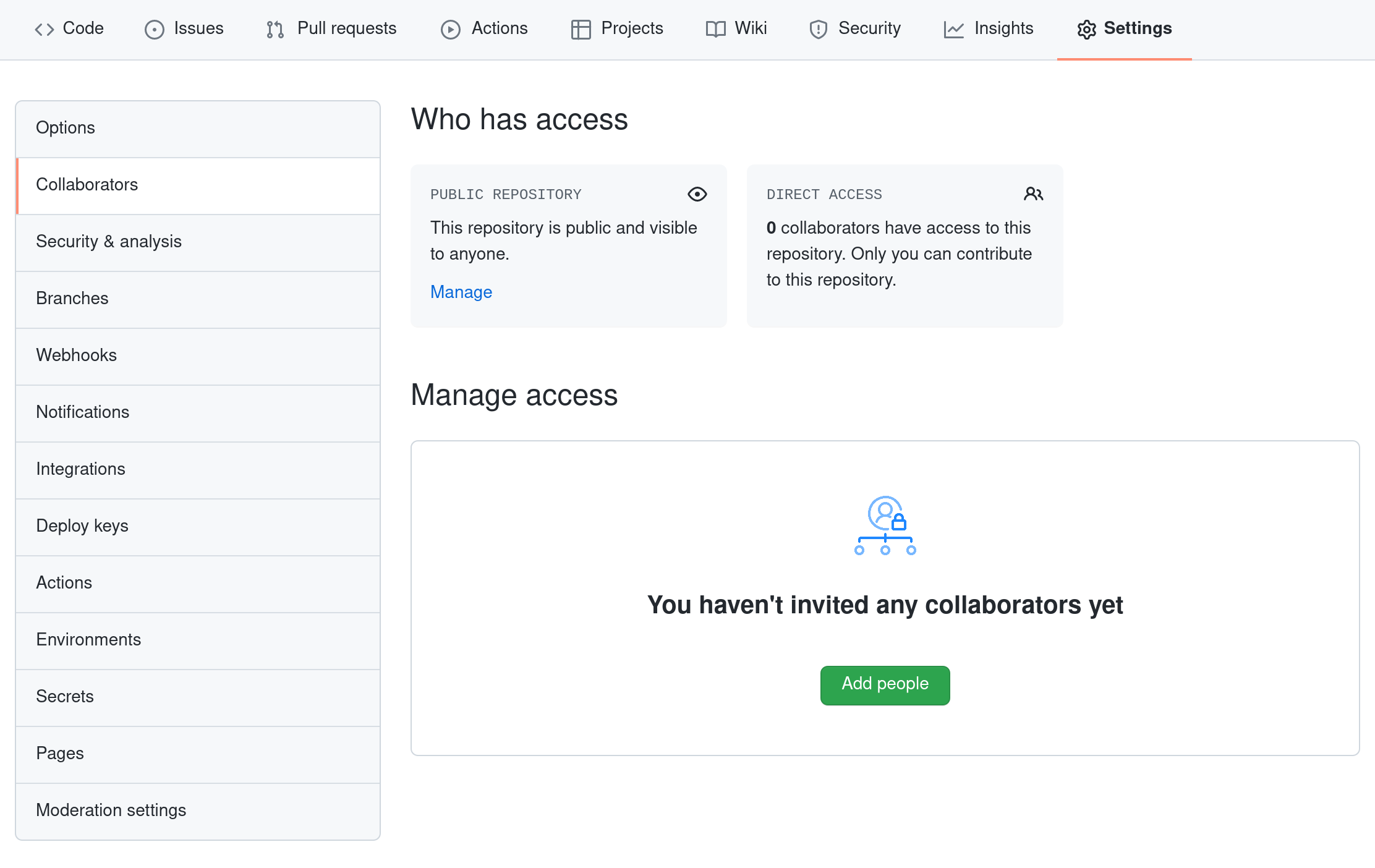
The Possessor needs to requite the Collaborator admission. On GitHub, click the settings button on the right, select Manage admission, click Invite a collaborator, then enter your partner's username.
To accept access to the Owner's repo, the Collaborator needs to become to https://github.com/notifications or bank check for email notification. Once there she can accept access to the Owner's repo.
Side by side, the Collaborator needs to download a re-create of the Owner's repository to her machine. This is chosen "cloning a repo".
The Collaborator doesn't want to overwrite her own version of planets.git, then needs to clone the Owner's repository to a unlike location than her own repository with the same proper noun.
To clone the Owner'south repo into her Desktop binder, the Collaborator enters:
$ git clone git@github.com:vlad/planets.git ~/Desktop/vlad-planets Replace 'vlad' with the Owner'southward username.
If you choose to clone without the clone path (~/Desktop/vlad-planets) specified at the end, you volition clone inside your ain planets binder! Make sure to navigate to the Desktop folder outset.
The Collaborator can now make a change in her clone of the Owner's repository, exactly the same way every bit nosotros've been doing before:
$ cd ~/Desktop/vlad-planets $ nano pluto.txt $ cat pluto.txt $ git add pluto.txt $ git commit -g "Add notes about Pluto" 1 file inverse, one insertion(+) create mode 100644 pluto.txt And so button the change to the Possessor's repository on GitHub:
Enumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 4, done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (iii/three), 306 bytes, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To https://github.com/vlad/planets.git 9272da5..29aba7c main -> principal Note that we didn't have to create a remote chosen origin: Git uses this name by default when nosotros clone a repository. (This is why origin was a sensible choice earlier when nosotros were setting up remotes past paw.)
Take a look at the Possessor's repository on GitHub again, and y'all should be able to see the new commit made past the Collaborator. You may need to refresh your browser to see the new commit.
Some more well-nigh remotes
In this episode and the previous one, our local repository has had a single "remote", chosen
origin. A remote is a copy of the repository that is hosted somewhere else, that we can push button to and pull from, and there's no reason that you have to work with only one. For example, on some big projects y'all might have your own copy in your own GitHub account (you lot'd probably call thisorigin) and also the main "upstream" project repository (let'south call thisupstreamfor the sake of examples). You would pull fromupstreamfrom fourth dimension to time to get the latest updates that other people take committed.Retrieve that the proper noun you requite to a remote only exists locally. Information technology's an alias that yous choose - whether
origin, orupstream, orfred- and not something intrinstic to the remote repository.The
git remotefamily of commands is used to fix and modify the remotes associated with a repository. Here are some of the near useful ones:
git remote -fivelists all the remotes that are configured (we already used this in the final episode)git remote add [name] [url]is used to add a new remotegit remote remove [proper noun]removes a remote. Notation that it doesn't affect the remote repository at all - it just removes the link to it from the local repo.git remote set-url [proper noun] [newurl]changes the URL that is associated with the remote. This is useful if information technology has moved, e.g. to a different GitHub account, or from GitHub to a different hosting service. Or, if we made a typo when adding information technology!git remote rename [oldname] [newname]changes the local alias by which a remote is known - its name. For example, one could apply this to alterupstreamtofred.
To download the Collaborator'south changes from GitHub, the Owner at present enters:
remote: Enumerating objects: 4, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. remote: Full 3 (delta 0), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (3/iii), done. From https://github.com/vlad/planets * branch principal -> FETCH_HEAD 9272da5..29aba7c chief -> origin/main Updating 9272da5..29aba7c Fast-frontward pluto.txt | 1 + 1 file changed, one insertion(+) create mode 100644 pluto.txt Now the three repositories (Owner'due south local, Collaborator's local, and Owner's on GitHub) are back in sync.
A Bones Collaborative Workflow
In practise, it is good to be sure that you have an updated version of the repository you are collaborating on, so you should
git pullbefore making our changes. The bones collaborative workflow would be:
- update your local repo with
git pull origin main,- make your changes and stage them with
git add together,- commit your changes with
git commit -chiliad, and- upload the changes to GitHub with
git push origin mainInformation technology is ameliorate to brand many commits with smaller changes rather than of one commit with massive changes: small commits are easier to read and review.
Switch Roles and Repeat
Switch roles and repeat the whole process.
Review Changes
The Owner pushed commits to the repository without giving any information to the Collaborator. How can the Collaborator find out what has inverse with command line? And on GitHub?
Solution
On the command line, the Collaborator tin use
git fetch origin mainto get the remote changes into the local repository, just without merging them. And then past runninggit diff main origin/mainthe Collaborator will see the changes output in the terminal.On GitHub, the Collaborator tin can go to the repository and click on "commits" to view the most recent commits pushed to the repository.
The Collaborator has some questions about one line change made by the Possessor and has some suggestions to propose.
With GitHub, it is possible to comment the diff of a commit. Over the line of code to annotate, a blue comment icon appears to open up a annotate window.
The Collaborator posts its comments and suggestions using GitHub interface.
Version History, Backup, and Version Control
Some backup software can keep a history of the versions of your files. They as well allows you to recover specific versions. How is this functionality different from version control? What are some of the benefits of using version control, Git and GitHub?
Key Points
git clonecopies a remote repository to create a local repository with a remote calledoriginautomatically prepare.
Source: https://swcarpentry.github.io/git-novice/08-collab/index.html
0 Response to "In Collaborator Why the First Upload Is Not Displayed in Ui"
Post a Comment